Industry 1.0 is the era of the steam engine, Industry 2.0 is the era of electrification, Industry 3.0 is the era of information technology, and Industry 4.0 is the era of using information technology to promote industrial change, that is, the era of intelligence.
Historically, every industrial revolution has been led by scientific breakthroughs and technological revolutions, bringing about great improvements in production efficiency, great changes in the mode of production and great leaps in productivity, and thus promoting the systematic reshaping of the international power pattern.
Raw materials are a key area for winning international competitive advantages and a mainstay of industrial base reengineering. In recent years, developed countries have actively deployed in related fields, and leading industry enterprises worldwide have accelerated their exploration of enabling business innovation applications such as the use of generative artificial intelligence. Whoever can take advantage of the first opportunity will be able to ride the wave. The raw materials industry, a new round of technological revolution and industrial change opportunities, to promote 5G, industrial Internet and other digital technologies and raw materials in-depth fusion, to promote the accelerated application of artificial intelligence in the raw materials industry, firmly grasp the initiative of development, and continue to enhance the international competitiveness of the raw materials industry.
Some industries have already entered the 4.0 era, but many others are in the 3.0 era. Whereas the last decade was dominated by digital transformation “from the outside in,” today’s business is more oriented toward leveraging the potential of data “from the inside out” with exponentially evolving technologies.
With the growing popularity of artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, automation, the Internet of Things (IoT), fifth-generation mobile communications technology (5G), and edge computing, the combination of these forces will inevitably reshape business architectures across industries.
Many enterprises have made significant efforts to create business platforms aimed at consolidating competitive advantages and establishing differentiating features. These platforms must be digitally connected at scale from the outside in and leverage cognitive technologies from the inside out.
What exactly is digital transformation? Digital transformation is a systematic project that requires total organizational mobilization and is a transformational journey driven by all three areas – business, organization and technology – working in tandem.
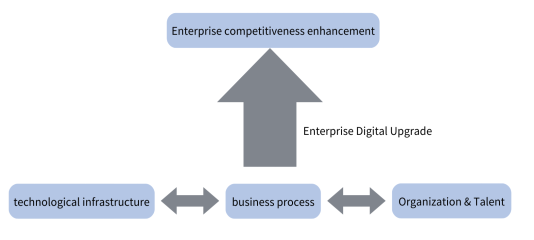
Business transformation refers to an enterprise’s ability to improve operational indicators through the digital transformation of the entire value chain, including the use of digital means to increase revenue in sales and R&D, the use of digital technology to reduce costs in purchasing, manufacturing, and support departments, and the use of digital methods to optimize cash flow in the supply chain and capital management. Successful business transformation requires a clear direction, a clear vision, and a clear roadmap for transformation in phases; at the same time, it focuses on the entire value chain and is driven by “net profit value” rather than simply pushing the transformation forward from the application of technology.
Technology transformation refers to building the technology architecture and technology ecosystem required for enterprise digital transformation. Technology architecture is the “bones” that support the piloting and rollout of digital business use cases, data architecture is the “blood” that ensures that “data-information-insight-action” can be realized, and the overall architecture needs to be built with the ultimate goal of digital transformation in mind. The overall architecture needs to be built with the ultimate goal of digital transformation in mind. The technology ecosystem is a circle of friends that encompasses a wealth of external digital intelligence and capabilities. Deployment of digital use cases, iterative innovation of digital technologies, and introduction of new technologies can only be achieved with the support of other partners in the technology ecosystem. Successful technology transformation requires a robust IoT architecture that creates and leads a thematic ecosystem of technology partners, enabling organizations to leverage their strengths and complement each other’s strengths to grow together.
Organizational and talent transformation refers to profound changes in organizational structure, operational mechanisms, talent training and organizational culture. Successful organizational transformation is a top-down change that requires the top management of the enterprise to define the goals, build a performance infrastructure, and become the “brain” that guides the direction of the transformation; to form a mapping of the transformation initiatives and financial indicators, and become the “eyes” that reflect the impact of the transformation; to establish consistent change management concepts and behaviors across the organization, and become the “heart” that leads the transformation up and down the organization. The mapping of transformation initiatives and financial indicators becomes the “eyes” that reflect the business impact of transformation; the establishment of consistent change management concepts and behaviors across the organization becomes the “heart” that leads the organization to change. On the other hand, enterprises need to focus on team building, bridging the capability gaps of employees, building a culture of digital knowledge learning and making it sustainable; they also need to promote the construction of digital capabilities and talent echelons, which form the “muscle” to promote large-scale promotion of transformation; and build agile organizations and teams to provide “Yogis” for the fast and good implementation and optimization of transformation initiatives. (c) Building agile organizations and teams to provide the “yogis” to implement and optimize transformation initiatives in a fast and efficient manner.
Technology architecture to match the business process change, technology architecture must be synergistic with the business process, whether the two sides are synergistic and synergistic whether appropriate to determine the success or failure of the digital change. The technology architecture should avoid over-design, but also avoid being led by the nose by the business, and whether the digital change can be put into practice also involves whether the organization and talents can take over and put the corresponding work in place. Therefore, digital change is a complex systems engineering, for the chief architect the requirements are very high, to understand the business of technical experts to assume the responsibility.
Digital transformation failure cases also abound, the main problems are: that only technology theory, is detached from their own business to follow the industry trend, organizations and talents are not willing to adapt to the new job requirements. For example: some years ago, the concept of a large center stage, was advocated as a life-saving straw, some companies followed the trend, the final structure is to make it difficult to ride the tiger, dust.
Digital transformation is suitable for all industries, especially those traditional ones that can use it to improve efficiency, optimize operations, enhance user experience, and even rebrand. Here are some industries that are particularly well-suited for digital transformation:
(1) Raw material industry: such as intelligent coal mines, intelligent oilfields, intelligent mining, etc. The raw material industry involves different fields such as petrochemical and chemical industry, iron and steel, non-ferrous metals, and building materials, etc. The concentration degree of each sub-field is different, the digitalization foundation is different, and scenario needs are different, and the digital transformation path is also quite different. For example, the petrochemical and chemical industry involves refining, coal chemical industry, fertilizer, chloralkali, tires, and many other sub-fields, non-ferrous metal involves copper, aluminum, lead, zinc, tungsten and other metal materials processing and production, building materials industry includes cement, glass, ceramics, glass fiber, gypsum board and other types of materials, product variety, a wide range, complex processes, digital transformation focus on their point of emphasis on the relevant instruments, intelligent equipment, industrial software and other requirements are different. They have different demands for related instruments, intelligent equipment, industrial software, etc.
(2) Manufacturing: Digital transformation can help the manufacturing industry to realize smart manufacturing, the Internet of Things and automated production, and improve production efficiency and output.
(3) Quality of products while optimizing supply chain and logistics management.
(4) Retail: Digital transformation can help the retail industry achieve multi-channel sales, personalized recommendations and enhanced customer experience. Through technologies such as e-commerce, mobile payments and data analytics, the retail industry can better understand customer needs and provide a personalized shopping experience.
(5) Financial sector: Digital transformation in the financial sector can drive innovative financial services, including digital payments, blockchain technology, smart investments and risk management. Through digital transformation, financial institutions can provide more convenient, efficient and secure services and develop new business models.
(6) Healthcare: Digital transformation can enable innovations in healthcare such as electronic medical records, telemedicine, health monitoring and data analytics. Through digital transformation, healthcare organizations can provide more personalized, efficient and accurate healthcare services and improve patient care and medical decision-making.
In addition, the catering industry is also an important area of digital transformation, they need to take advantage of the digitalization of the wind of the times, and actively seek to suit their digital transformation methods, build their online shopping malls, establish their brand of private domain traffic pools, and realize the integration of online and offline operations.
Overall, Industry 4.0 + Raw Materials is the new outlet for the future of IT, and digital transformation offers companies the opportunity to improve efficiency, competitiveness, and innovation, especially for those willing to embrace change and adopt new technologies that will enable them to gain a significant advantage in the digital age.
However, industrial digital transformation is a gradual process, the pace and priority of different industries are not the same, so there will not be a swarm of big on the fast dry wave of the scene, and even less likely to be everywhere is the opportunity of the “wind”, the need to penetrate the specific industry for deep cultivation, to improve business efficiency and process optimization.
